Table of contents
What can KSK Analysis Planning Design do for you in the field of damage analysis?
Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering is a fascinating field that presents both technical and legal challenges. It offers engineers the opportunity to analyze existing products and develop new innovations. This article highlights the various aspects of reverse engineering, from its definition and application to the legal and ethical considerations surrounding it.
Old but new.
Trust our expertise in reverse engineering and let us work together to take your “old” systems and machines to the next level! Feel free to contact us for individual advice on the following topics:
- Detailed 3D scans and modeling
- Technical analyses and feasibility studies
- Creation of documentation and technical drawings
- Support in the optimization and redesign of systems
Your contact

Björn Brüningk-Weißhar, M. Sc.
Head of Engineering
+49 (0) 2364 60897 -20
Back to the future.
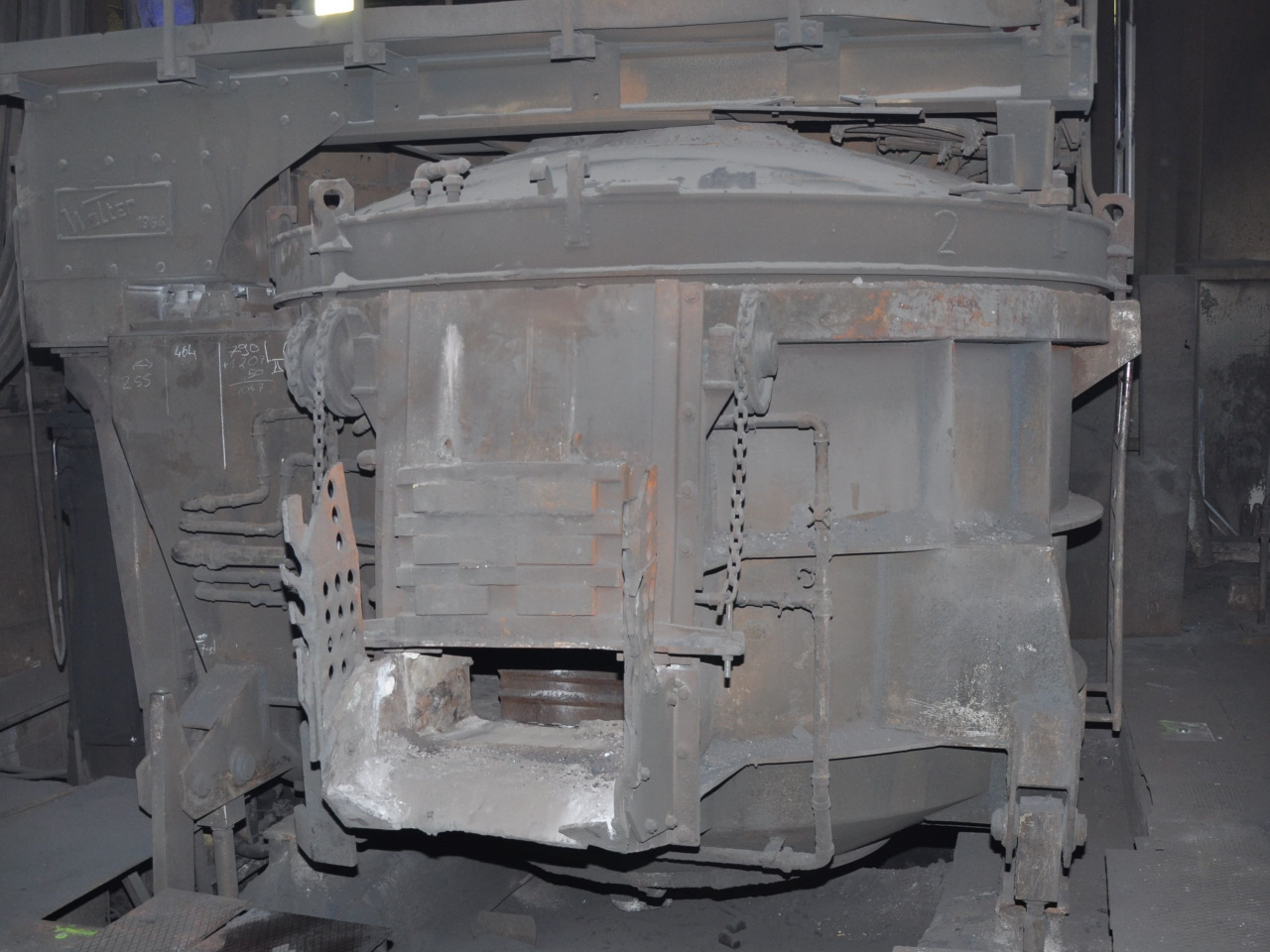
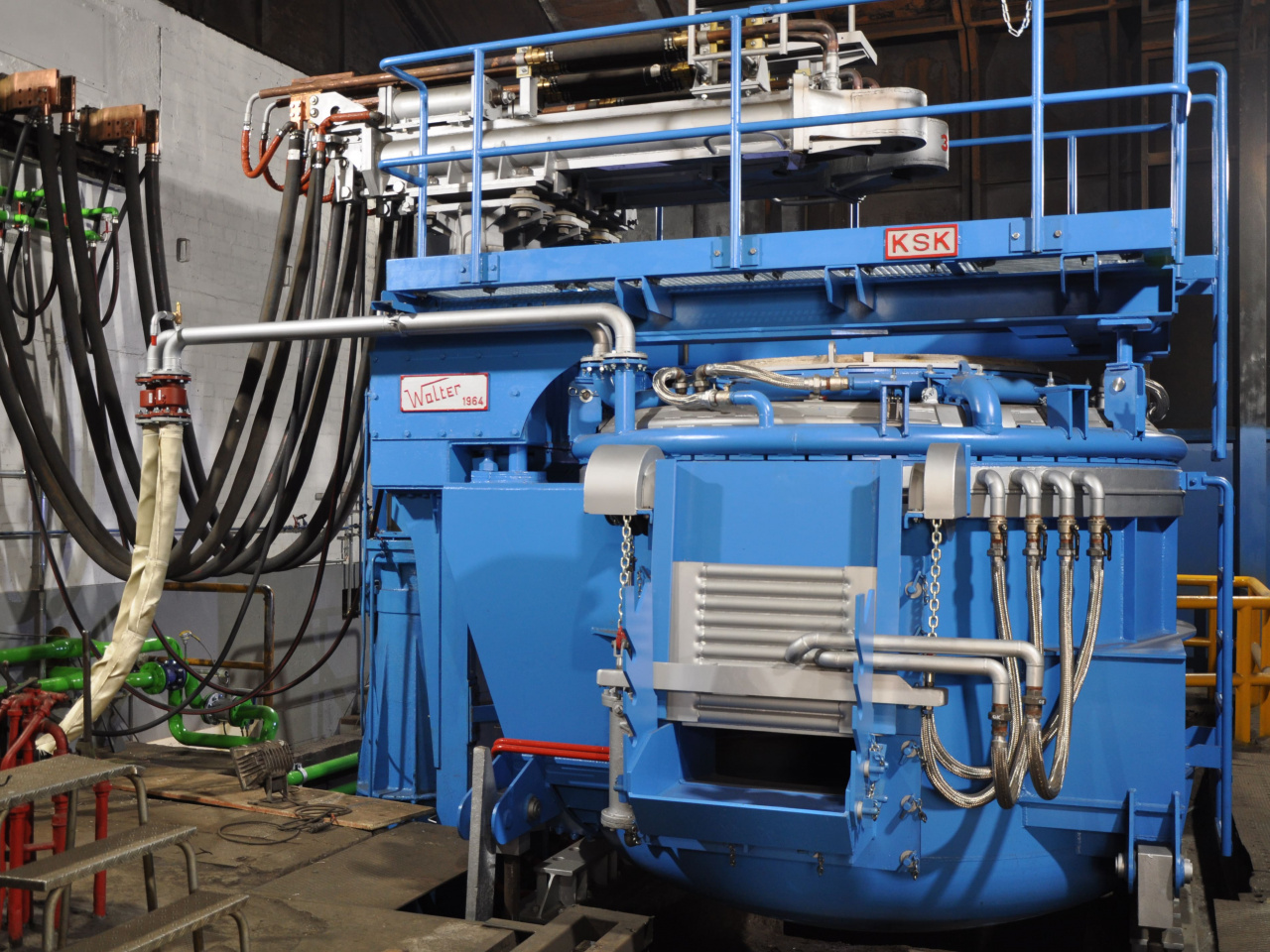
- Discover the future of plant engineering with our reverse engineering service and stay competitive and at the cutting edge in our fast-moving industry! We offer you the opportunity to replicate existing plants and systems and bring them up to the state of the art.Why reverse engineering?Then take advantage of our expertise to modernize your products and processes and secure a decisive advantage in the market.
- You can see how this works in the specific example of an electric arc furnace in the images below or here in the linked technical article.What is reverse engineering and how is it used?Definition and purpose of reverse engineeringReverse engineering refers to the process of dismantling a product or system in order to understand its structure, functionality, or manufacturing method. The main purpose of reverse engineering is to analyze the functionality of an existing product in order to reproduce or optimize it. This process can be carried out manually or with special tools and is widely used in many industries, including software development and mechanical engineering.Typical applications and examples
- Reverse engineering can be applied in numerous areas, including software, hardware, and electronics. A classic example is the analysis of source code to gain a better understanding of the program structure and functionality. In electronics, it can be used to examine and reproduce electronic components. Reverse engineering also plays an important role in product development, as it enables engineers to improve existing products and develop innovative solutions.
- Advantages of reverse engineeringReverse engineering offers many advantages, including the ability to optimize existing products and create new innovations. It can also help improve the usability of a product and expand its functionality. In addition, it enables engineers to develop new ideas by analyzing existing products and increase efficiency in product development.Is reverse engineering legal?
- Legal framework in software developmentThe legality of reverse engineering varies depending on the country and legal framework. In software development, laws on reverse engineering can differ from country to country. In many countries, certain forms of reverse engineering are permitted, while others are strictly regulated or prohibited. A key consideration is whether it is used for legitimate purposes, such as improving interoperability or protecting against malware.
- Legal aspects of reverse engineering hardwareSimilar legal considerations apply to reverse engineering hardware as to software development. Analyzing hardware components to understand their structure and functionality can be legally controversial, especially when it comes to replicating or modifying existing products. The legal framework varies greatly here as well and often depends on how the reverse engineering is carried out and for what purpose.Differences between countries, especially in Europe
- In Europe, there are a variety of legal regulations governing reverse engineering. The legal framework can vary significantly between countries, with some European laws allowing reverse engineering under certain conditions, while others restrict it. These differences are reflected in the diversity of jurisdictions and influence how engineers and companies can use reverse engineering in their development processes.How does reverse engineering work for hardware?
- Process and tools for reverse engineering hardwareThe process of reverse engineering hardware involves the systematic analysis of components and their functionality. Engineers use specialized tools to examine the mechanical and electronic structure of a product. This analysis can be done manually or with computer-aided methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of the product and efficiently replicate or optimize it.
- Challenges and solutions in electronicsReverse engineering poses particular challenges in the field of electronics, as electronic components are often complex and difficult to analyze. Engineers must develop innovative methods to understand the functionality and structure of circuits and components. Solutions include the use of advanced analysis tools and techniques to overcome the challenges of modern electronics and develop new products.
- Examples of products and componentsTypical examples of reverse engineering in electronics include the analysis of microprocessors, memory chips, and other complex components. These components are often examined to understand their functionality and find ways to produce them more efficiently or cost-effectively. Reverse engineering can also help identify weaknesses in existing products and fix them.
- What role does source code play in reverse engineering?Analysis and restoration of source codeSource code plays a crucial role in the reverse engineering of software. By analyzing the code, engineers can understand the structure and functionality of a program and, if necessary, restore or improve it. Restoring source code requires a deep understanding of programming languages and structures, as well as the use of special tools for code analysis.
- Importance of source code for product developmentIn product development, source code is crucial because it forms the basis for how a software product works. A deep understanding of the source code enables developers to optimize existing programs, integrate new features, and improve usability. Reverse engineering can help obtain the information needed to achieve these goals.
- Technical and legal considerationsWhen reverse engineering source code, both technical and legal considerations must be taken into account. From a technical standpoint, analyzing the code requires specialized knowledge and tools. From a legal standpoint, developers must ensure that their activities comply with reverse engineering laws and do not infringe on any copyrights or patents.What are the ethical and innovative considerations involved in reverse engineering?
- Innovation and optimization through reverse engineeringReverse engineering can be a powerful tool for innovation and optimization. By understanding existing products, engineers can develop new approaches to improve their performance and create innovative solutions. This process not only promotes technological development, but also contributes to increased efficiency in production and design.Ethical considerations and user-friendliness
- Ethical considerations play a central role in reverse engineering. Developers must ensure that their approaches are fair and transparent and respect the rights of the original developers. In addition, the focus should be on improving usability and providing added value for users without compromising the integrity of the original product.Contribution to the industry and mechanical engineering
- Reverse engineering makes an important contribution to the industry and mechanical engineering by opening up new opportunities for product development and innovation. It enables engineers to analyze and improve existing technologies, leading to advances in the efficiency and functionality of machines and devices. This process drives the industry forward and promotes the development of new, innovative products.


Analysis and Advice

Project management

Commissioning of Plants
Safety Engineering
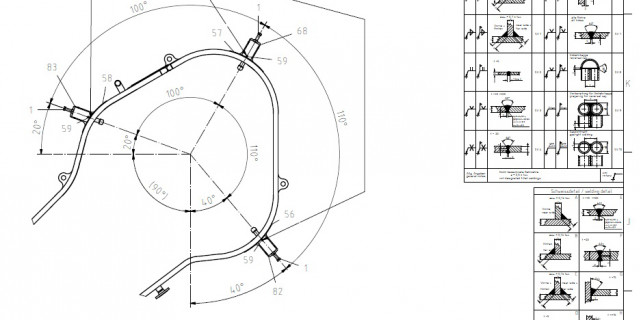
Technical Documentation
Conceptual Engineering

Conceptual Engineering
Engineering Office
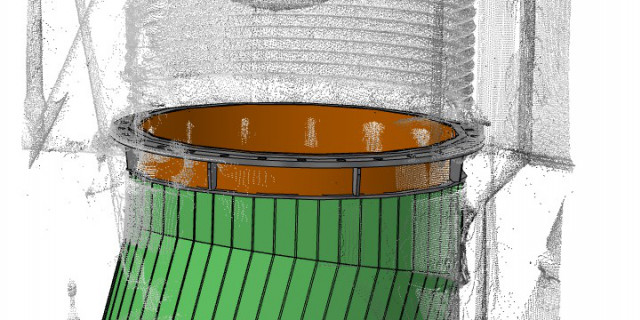
3D Measurement
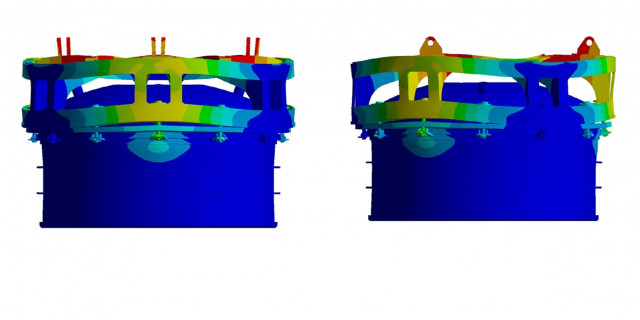
FEM Simulation

CFD Simulation

Structural Steel Statics
Table of contents
- Q: What is reverse engineering?
- Q: How is reverse engineering used?
- Q: Is reverse engineering legal?
- Q: What tools are used in reverse engineering?
- Q: Can reverse engineering help restore old systems?
- Q: What role does reverse engineering play in the development of new products?
- Q: Why do some companies make it difficult to understand their products?
- Q: What are the ethical considerations of reverse engineering?
- Q: How can reverse engineering benefit software development?
Q: What is reverse engineering?
A: Reverse engineering is the process of analyzing a product or system to understand its structure, components, and how it works. It is often used to reconstruct the design or to verify software and electronic components. Reverse engineering can be applied in various fields, including software development, hardware design, and even biotechnology. In software development, reverse engineering is often used to modernize older programs or to uncover security vulnerabilities in a system. Developers analyze the source code to understand the logic and functionality of the software and make improvements or adjustments.
In the hardware field, reverse engineering enables the physical structure of devices to be understood. Engineers can reconstruct the circuit diagrams and physical architecture of a product, which can be useful for manufacturing replacement parts or ensuring compatibility with other systems.
In biotechnology, reverse engineering can be used to understand and reproduce biological processes. Researchers analyze biological systems to decipher their mechanisms, which can lead to the development of new drugs or therapies.
However, there are also legal and ethical considerations associated with reverse engineering. In some countries, it is restricted by law, particularly when it comes to circumventing copy protection mechanisms or infringing patents. It is therefore important to be aware of and comply with the legal framework before engaging in reverse engineering.
In summary, reverse engineering is a powerful tool that can drive innovation and extend the life of products, but it requires a deep understanding of the technologies involved and compliance with legal regulations.
Q: How is reverse engineering used?
A: Reverse engineering can be applied in many ways, including analyzing computer programs to determine the source code or examining electronic components to understand their structure. Reverse engineering can be applied in many ways, including analyzing computer programs to determine the source code or examining electronic components to understand their structure. In addition, reverse engineering is also used in other areas, such as the automotive industry, where it is used to understand and potentially improve the design of vehicle parts. In the pharmaceutical industry, reverse engineering can be used to analyze the composition of drugs, particularly when developing generic versions of existing drugs.
In software development, reverse engineering is often used to understand how older systems work, especially when the source code is no longer available or the original developers are no longer available. This can be crucial for identifying and fixing security vulnerabilities or for updating systems and integrating them with newer technology.
Another important area is security research, where reverse engineering is used to identify and fix vulnerabilities in software. Security researchers analyze programs to discover exploits that could be exploited by malicious actors. This is crucial for developing patches and security updates that protect the integrity of software and systems.
In electronics, reverse engineering enables a detailed understanding of circuits and their components. This can help develop more cost-effective or efficient designs while ensuring compatibility with existing systems. It also plays a role in the repair and maintenance of devices for which the original manufacturer's documentation is not available.
However, reverse engineering is not without legal and ethical challenges. It is important to consider the legal provisions relating to copyright, patents, and intellectual property protection. In many cases, it is necessary to obtain permission from rights holders or ensure that use is within the scope of legal exceptions.
Q: Is reverse engineering legal?
A: The legality of reverse engineering varies depending on the jurisdiction of many countries. In the European Union, there are specific regulations for the protection of copyrights and patents that must be taken into account. In the European Union, reverse engineering is permitted under certain conditions, in particular when it is necessary for the interoperability of software products. The relevant regulation can be found in the EU Software Directive (Directive 2009/24/EC), which stipulates that the decompilation of a program by its lawful acquirer or an authorized person is permitted if this is necessary to understand the functioning of a program and to make it interoperable with other programs.
However, certain conditions must be met: The acquirer must have the right to use the program, the information necessary to achieve interoperability must not be readily available elsewhere, and the reverse engineering process must not go beyond what is necessary to achieve interoperability.
Furthermore, it is not permitted to use the knowledge gained for other purposes or to pass it on to third parties, unless this is necessary for interoperability. Nor may any information about the reverse engineering be published that could damage the original program or harm the interests of the author.
In other countries, such as the US, the laws on reverse engineering vary. There, the principle of fair use or the doctrine of implied license may play a role, but the legal landscape is more complex and often varies from case to case.
Companies should therefore carefully review the legal framework in each country and seek legal advice if necessary before using reverse engineering as a strategy to ensure that they comply with legal requirements and do not infringe any copyrights or patents.
Q: What tools are used in reverse engineering?
A: There are many technical tools that engineers use in reverse engineering, including source code analysis software, devices for examining electronic components, and tools for structure reconstruction. Some of the most common software tools for source code analysis include decompilers, debuggers, and disassemblers. These tools enable engineers to convert the machine code of an application into a human-readable form. This allows them to understand how a program works and identify vulnerabilities or areas for optimization.
Oscilloscopes, logic analyzers, and multimeters are commonly used to examine electronic components. These devices allow engineers to measure and analyze the electrical properties of a circuit to understand its functionality and design.
Tools for structural reconstruction, such as 3D scanners and CAD software, are also crucial. They enable physical objects to be converted into digital models, which can then be used for analysis or as a basis for redesign.
In addition, specialized software solutions such as simulation programs also play an important role. These allow the behavior of a system to be modeled under various conditions without having to perform physical tests.
Overall, reverse engineering is a complex process that requires a combination of technological expertise, creativity, and the right tools to be carried out successfully.
Q: Can reverse engineering help restore old systems?
A: Yes, reverse engineering can also help analyze outdated or legacy systems to understand their functionality and, if necessary, reconstruct or modernize them. Yes, reverse engineering can also help analyze outdated or legacy systems to understand their functionality and, if necessary, reconstruct or modernize them. This is particularly useful when the original documentation is missing or incomplete. By analyzing existing systems, companies can gain important information that is necessary to update the systems or integrate them seamlessly into modern infrastructures.
In addition, reverse engineering can help identify and fix security vulnerabilities. This is a crucial advantage, especially for older systems that may no longer be maintained by the original developers. By understanding the underlying architecture and code, companies can discover potential vulnerabilities and take appropriate measures to increase security.
Another advantage is the ability to optimize systems and improve their performance. By analyzing the existing code, inefficient processes can be identified and optimized, resulting in better overall performance. Reverse engineering also makes it possible to identify functions that can be automated or modernized to better meet the demands of today's digital world.
Overall, reverse engineering is a valuable tool for addressing the challenges associated with maintaining and modernizing legacy systems. It enables companies to fully leverage the potential of their existing infrastructures and ensure that they are future-proof.
Q: What role does reverse engineering play in the development of new products?
A: Reverse engineering allows engineers to analyze existing products to identify their strengths and weaknesses, which can be helpful when developing new products or improving existing ones. Reverse engineering allows engineers to analyze existing products to identify their strengths and weaknesses, which can be helpful when developing new products or improving existing ones. By understanding the underlying mechanisms and technologies, engineers can develop more innovative and efficient solutions. This can also help optimize production processes and reduce costs.
Another advantage of reverse engineering is its ability to solve compatibility issues. Engineers can ensure that new products work seamlessly with existing systems, which is particularly important in industries such as information technology and the automotive industry. In addition, reverse engineering can extend the life of existing products by developing replacement parts that are no longer manufactured.
Despite its numerous advantages, however, there are also challenges and ethical considerations associated with reverse engineering. Intellectual property rights must be respected in order to avoid legal conflicts. Companies must ensure that their practices comply with applicable laws and regulations and respect the rights of the original developers.
Overall, reverse engineering plays a crucial role in modern product development, helping to drive innovation and support technological progress.
Q: Why do some companies make it difficult to understand their products?
A: Some companies deliberately make their products difficult to understand in order to protect their intellectual property rights and prevent imitation by competitors. They often do this by using complex technical jargon that obscures product features or by employing proprietary technologies that are difficult to decipher. These strategies can be effective in the short term, but they can also create barriers to entry for new competitors. They often do this by using complex technical jargon that obscures product features or by employing proprietary technologies that are difficult to decipher. These strategies can be effective in the fast-paced, innovation-driven business world to maintain competitive advantages.
However, this secrecy can also have negative effects. Customers may become frustrated if they have difficulty using the products or understanding their benefits. This could lead to a loss of trust and affect customer loyalty. In addition, it can become more difficult for companies to enter into partnerships or expand into new markets if potential partners have difficulty understanding the technologies or products on offer.
A balancing act is required: companies must protect their innovations, but they must not neglect transparency and access for their customers and business partners. Clear and effective communication about the unique benefits of a product, without revealing sensitive details, is the key to sustainable business success.
Q: What are the ethical considerations of reverse engineering?
A: Reverse engineering raises ethical questions, particularly when it comes to protecting intellectual property and data privacy. Companies and engineers must carefully weigh the legal and ethical implications before deciding to use reverse engineering techniques. On the one hand, reverse engineering can help drive innovation by enabling existing technologies to be analyzed and improved. On the other hand, there is a risk that intellectual property may be infringed by decrypting protected technologies or software licenses.
In addition, reverse engineering can expose sensitive data that was originally protected. This raises questions about data privacy and data security, especially at a time when cybersecurity is of paramount importance. Companies must ensure that they comply with legal requirements and take appropriate measures to protect the privacy and security of user data.
Another ethical aspect is transparency. Companies should disclose the extent to which they engage in reverse engineering and what data is used in the process. This transparency can strengthen consumer confidence and ensure that ethical standards are upheld.
Overall, the use of reverse engineering requires a careful balance between promoting innovation and protecting rights and data. Companies should work with legal experts and ethicists to develop guidelines that ensure their practices are both legal and ethical.
Q: How can reverse engineering benefit software development?
A: Reverse engineering can be used to analyze the source code of old or poorly documented programs in order to update or improve them and ensure that they are compatible with modern standards. Reverse engineering can also be used to identify and fix security vulnerabilities in software. By analyzing how a program works, developers can discover vulnerabilities that could be exploited by potential attackers. In addition, reverse engineering provides an understanding of how different software components interact, which is particularly useful when integrating or extending existing systems.
Another area of application is interoperability. Companies can use reverse engineering to ensure that new software solutions are compatible with existing systems without the original source code being available. This is particularly important in environments where different software platforms need to work together seamlessly.
In product development, reverse engineering can also be used to analyze competitors' products in order to develop better or more cost-effective alternatives. However, it is important to consider legal and ethical aspects in order to avoid infringing patents or copyrights.
Overall, reverse engineering offers many opportunities to optimize, secure, and further develop software and systems while promoting technological progress and innovation.


