
Table of contents
-
What can KSK Analysis Planning Design do for you in the area of plant commissioning?
- The plant is up and running.
- Your contact
What can KSK Analysis Planning Design do for you in the area of plant commissioning?
The plant is up and running.
Everything is assembled, and the production team is waiting. When can we finally get started? After all, every minute of downtime costs money. The pressure on everyone involved during commissioning is often correspondingly high. This is also the case for us, of course. Hesitation and despair will not get us anywhere. But neither do arrogance and going it alone. As a medium-sized company, we have found that as allies, customer and supplier can achieve much more in a project, even in critical situations (during commissioning), than if everyone involved insists rigidly on interfaces, contracts, or being right. For us, as for you, one thing is always paramount: The plant must run. Our entire team of electricians and mechanics on site and in the office is committed to this goal with all their experience and technical know-how.
Your contact

Dipl.-Ing. (TU) Michael Rosenthal
Project Engineer
+49 (0) 2364 10539-24
What is the process of commissioning plants?
Efficient commissioning of systems: checklists and process engineering details
The commissioning of systems is a crucial step in the life cycle of technical systems, marking the transition from the construction and assembly phase to regular operation. It ensures that the systems function properly and efficiently by checking all components for full performance and ensuring compliance with safety and quality standards. This process is of central importance in many industries, from chemicals to steel, in order to protect investments in new plants and ensure their long-term performance.
What steps does the commissioning of process plants involve?
The commissioning of process plants involves a number of steps that must be systematically planned and carried out. First, the process engineering systems are planned and constructed, taking into account all specific requirements of DIN VDE. This is followed by the assembly and commissioning of the systems, during which it is ensured that the mechanical and electrical systems are installed correctly. After assembly, the actual commissioning begins, which consists of various phases such as pre-commissioning, commissioning, and final acceptance. During these phases, all system components are checked for functionality and completeness to ensure that the plant is commissioned properly.
How is operational readiness ensured?
To ensure that a plant is ready for operation, it is important that all technical and mechanical systems are thoroughly tested. This includes both technical measurements and systematic checks of all components. The functionality of the plant must be fully guaranteed before it is put into regular operation. Engineers play a crucial role here, working responsibly from specification to acceptance and ensuring that everything functions properly. The documentation of all tests and inspections serves as proof of successful commissioning and helps to identify and rectify any defects at an early stage.
What role does quality assurance play in this process?
Quality assurance is an integral part of the commissioning process. It ensures that all steps are carried out in accordance with the prescribed standards and specifications. Quality assurance measures, such as the systematic inspection of individual components and the performance of tests, are crucial to ensuring the full functionality and safety of the system. In addition, quality assurance helps to identify and correct any deviations at an early stage, which increases the efficiency and safety of commissioning.
How do you create checklists for successful commissioning?
What elements should be included in a commissioning checklist?
A commissioning checklist should cover all the essential steps and tests required for the successful commissioning of a system. This includes checking the mechanical and electrical systems, ensuring compliance with safety standards, and documenting all tests performed. Specific requirements of DIN VDE should also be taken into account. A well-structured checklist helps to maintain an overview and ensure that no step is overlooked. It serves as a guide for engineers and technicians to ensure the proper functioning of the system.
How can documentation be carried out during commissioning?
Documentation during commissioning is crucial for tracking progress and ensuring quality. All tests and inspections carried out must be properly documented to serve as proof of successful commissioning. Documentation should be systematic and detailed so that it is understandable and traceable for all parties involved. Modern digital tools can help with this by enabling efficient recording and management of all relevant data.
What are the best practices for creating checklists?
Best practices for creating checklists include involving all relevant stakeholders to ensure that all aspects of commissioning are taken into account. The checklist should be clear and concise and cover all necessary steps for commissioning. It is also advisable to update the checklist regularly and adapt it to new technologies and standards. Close cooperation between engineers, technicians, and quality assurance officers can help ensure that the checklist meets all relevant requirements and that commissioning is carried out efficiently.
How does quality assurance contribute to the commissioning of plants?
Which quality assurance measures are crucial?
Important quality assurance measures during commissioning include the systematic inspection of plant components, the performance of functional tests, and the monitoring of compliance with safety and quality standards. These measures ensure that the plant functions properly and meets all requirements. It is also crucial that quality assurance works closely with engineering until commissioning to identify and eliminate potential sources of error at an early stage.
How is the functionality and complete mechanics of the systems ensured?
The functionality and complete mechanics of the systems are ensured through systematic tests and inspections. These include both mechanical and electrical tests to ensure that all systems interact properly. Quality assurance plays a central role here by monitoring and verifying compliance with the specified specifications. Regular maintenance and inspection programs also contribute to the long-term functionality of the plant.
How can the systematic inspection of components be carried out?
Components are systematically checked through detailed inspections and tests designed to ensure the proper functioning and safety of the plant. These checks should be carried out according to a set schedule and cover all relevant aspects of commissioning. Close cooperation between engineers and quality assurance officers is essential to ensure that all components meet the requirements and that the plant can be operated efficiently.
What are the challenges involved in commissioning process engineering plants?
What are the common problems encountered during construction and assembly?
The construction and assembly of process engineering plants can present a number of challenges. Common problems include delays in the delivery of components, unexpected technical difficulties, and deviations from the original specifications. These problems can significantly impact the commissioning schedule and require careful planning and coordination to be resolved in a timely manner.
How do you deal with unexpected technical difficulties?
Dealing with unexpected technical difficulties requires flexibility and quick problem-solving skills. Close cooperation between engineers and project managers is crucial to finding solutions and minimizing the impact on the commissioning process. It is often necessary to make adjustments at short notice or develop alternative solutions to avoid jeopardizing commissioning.
What role does the speaker play in solving these challenges?
The speaker plays an essential role in solving challenges during commissioning by acting as the central point of contact for all parties involved. He coordinates communication between the various teams and ensures that all information is passed on in a timely and complete manner. They are also responsible for documenting and tracking problems and their solutions in order to better address future challenges.
How can the efficiency of plant commissioning be increased?
What strategies lead to more efficient commissioning of new plants?
Several strategies can be used to increase the efficiency of new plant commissioning. These include the early involvement of all relevant stakeholders, detailed planning, and the use of checklists to ensure that all steps are carried out correctly. In addition, modern technologies and digital tools can increase efficiency by improving communication and documentation and enabling problems to be identified and solved more quickly.
How can an engineer optimize the process from specification to acceptance?
An engineer can optimize the process from specification to acceptance by ensuring that all technical requirements are clearly defined and communicated. Close cooperation with project management and quality assurance is also crucial to ensure that all aspects of commissioning are carried out efficiently and properly. Through regular reviews and adjustments to the project plan, the engineer can ensure that commissioning is completed on time and within budget.
What technical measurements are necessary to ensure efficiency?
Various technical measurements are necessary to ensure the efficiency of commissioning. These include functional tests of the mechanical and electrical systems and verification of compliance with safety and quality standards. These measurements should be carried out systematically and regularly to ensure that the plant is functioning properly and meets all requirements. Comprehensive documentation of these measurements is also crucial to serve as proof of successful commissioning and to enable future optimizations.


Analysis and Advice

Project management
Safety Engineering
Technical Documentation
Conceptual Engineering

Conceptual Engineering
Engineering Office
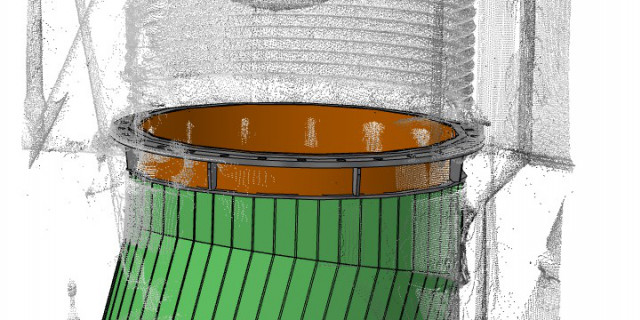
3D Measurement
Reverse Engineering
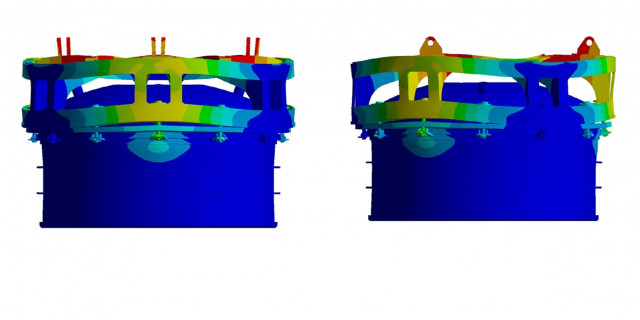
FEM Simulation

CFD Simulation

Structural Steel Statics
Table of contents
- Q: What is meant by plant commissioning?
- Q: Who is typically involved in the commissioning of process plants?
- Q: What are the challenges involved in commissioning plants?
- Q: How long does it typically take to commission a plant?
- Q: What happens after commissioning is complete?
- Q: What documentation is required for commissioning?
- Q: What qualifications are required for commissioning plants?
- Q: How can you ensure that a plant complies with legal requirements?
Q: What is meant by plant commissioning?
A: Plant commissioning refers to the process in which a plant, for example a process plant, is put into operation and tested for the first time to ensure that it functions properly and meets the requirements. Plant commissioning refers to the process in which a plant, such as a process engineering plant, is started up and tested for the first time to ensure that it functions properly and meets the requirements. This process is an essential part of plant construction and involves several steps that must be carefully planned and carried out.
At the start of commissioning, a comprehensive check of all systems and components is carried out to ensure that they are correctly installed and connected to each other. This includes checking mechanical, electrical, and control elements. After this preliminary check, the individual systems are put into operation step by step, starting with simple function tests, followed by more complex tests under operating conditions.
An important aspect of commissioning is the calibration and adjustment of the control systems to ensure optimal performance of the plant. This also includes checking the safety mechanisms to ensure the protection of personnel and the environment.
After successful completion of the tests, the plant is usually subjected to a trial run, during which it operates under real conditions for a certain period of time. During this phase, all processes are closely monitored and adjustments are made as necessary to optimize efficiency and ensure compliance with all relevant regulations.
Finally, detailed documentation is prepared, including all steps taken and test results. This documentation serves as proof of proper commissioning and can be used as a reference for future maintenance or optimization work.
The successful commissioning of a plant is crucial for its long-term performance and reliability. It requires close cooperation between engineers, technicians, and operators to ensure that all aspects of the plant meet the specified requirements and operate efficiently.
Q: Who is typically involved in the commissioning of process plants?
A: The commissioning of process plants often involves engineers and technicians who have worked for many years in the chemical or gas industry designing plants. Auditors and consultants such as Klaus H., who specialises in contract drafting and processing, may also be involved. These experts contribute their extensive knowledge and experience to ensure that the plants are operated efficiently, safely, and in an environmentally friendly manner. Engineers and technicians are usually responsible for technical planning and implementation, while auditors and consultants such as Klaus H. ensure that all legal and contractual aspects are carefully taken into account.
The commissioning process often begins with detailed planning, during which all necessary steps are defined. This includes reviewing technical specifications, conducting safety tests, and training operating personnel. Engineers work closely with technicians to ensure that all systems are properly installed and functional.
Auditors play a crucial role in verifying compliance with legal regulations and internal standards. They carry out regular inspections and prepare reports that identify potential risks or deviations. Consultants such as Klaus H. support the team by providing sound recommendations for optimizing processes and ensuring that all contractual obligations are met.
The collaboration between these different disciplines is crucial to the successful operation of the plant. By sharing knowledge and experience, they help to ensure that the plant not only meets current requirements but is also equipped to meet future challenges.
Q: What are the challenges involved in commissioning plants?
A: Commissioning involves many uncertainties, such as unforeseeable technical problems, delays, or deviations from the planned specifications. In addition, legal regulations must be complied with, which can further complicate the process. Careful planning and risk management are crucial to meeting these challenges. This includes identifying potential risks early on and developing strategies to mitigate them. Regular testing and quality control can help identify and resolve technical issues at an early stage.
Another important aspect is close cooperation with all parties involved, including suppliers, contractors, and authorities. Clear communication and coordination can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure that everyone involved is on the same page.
In addition, staff training can ensure that all employees have the necessary knowledge and skills to carry out commissioning efficiently and safely. Flexibility and a willingness to adapt plans as needed are also crucial to being able to respond to unexpected challenges.
Overall, the successful commissioning of a project requires a holistic approach that takes into account both technical and organizational aspects to ensure that all objectives are achieved on time and within budget.
Q: How long does it typically take to commission a plant?
A: The duration of commissioning can vary greatly. Some of the factors that can influence the duration of commissioning are:
1. **Plant size and complexity**: Larger and more technically complex plants usually require more time for commissioning, as more systems and components need to be integrated and tested.
2. **Availability of resources**: The availability of qualified personnel and necessary materials or equipment can significantly influence the time frame. Delays in procurement can prolong the process.
3. **Team experience**: An experienced team can make the commissioning process more efficient, as it usually takes less time to identify and resolve issues.
4. **Coordination with other projects**: If commissioning needs to be coordinated with other projects or construction work, this can lead to additional delays.
5. **Regulatory requirements**: In some cases, certain regulatory or safety-related tests must be carried out, which can take additional time.
6. **Unforeseen problems**: Technical difficulties or unexpected challenges during commissioning can also affect the timeframe.
It is important to consider these factors when planning commissioning and to allow for buffer times if necessary to ensure that the project remains on schedule. Close cooperation between all parties involved and careful planning can help to optimize the process and minimize potential delays.
Q: What happens after commissioning is complete?
A: Once commissioning is complete, the plant is officially put into operation and those responsible check that it is running efficiently and safely. This is often referred to as the “moment of truth.” Once commissioning is complete, the plant is officially put into operation and those responsible check that it is running efficiently and safely. This is often referred to as the “moment of truth.” During this critical phase, all systems and components are tested under real operating conditions to ensure that they meet the requirements and that no unexpected problems arise.
Engineers and technicians carefully monitor the performance of the plant and analyze data to identify potential weaknesses or areas for optimization. If any irregularities or defects are found, they are immediately documented and appropriate corrective measures are initiated.
Successfully passing the “hour of truth” means that the plant not only meets the technical specifications, but can also be operated reliably and sustainably. This is a crucial step in gaining the trust of investors, operators, and other stakeholders.
After the plant has been successfully commissioned and accepted, a training phase for the operating personnel usually follows. These training courses ensure that all employees are familiar with the specific processes and safety protocols of the new plant. In addition, a maintenance plan is drawn up to ensure the long-term efficiency and safety of the plant.
Overall, the “moment of truth” marks the transition from theory to practice and is a crucial moment in the life cycle of a plant. It forms the basis for smooth and successful operation in the years to come.
Q: What documentation is required for commissioning?
A: Comprehensive documentation is crucial for tracking all steps and tests. The number of illustrations, plans, and reports can be extensive in order to make the entire process transparent and traceable. The documentation should be clearly structured and easily accessible so that all parties involved can access it at any time. Essential components include detailed descriptions of the methods used, the equipment used, and the results of the tests and analyses. Each illustration and report should be clearly labeled and dated to avoid any confusion.
It is also helpful to include a summary or table of contents that provides a quick overview of the information contained. This allows users of the documentation to quickly find the sections that are relevant to them. Well-designed documentation not only supports traceability and quality assurance, but also facilitates the further development and optimization of future projects.
Regular reviews and updates of the documentation ensure that it is always up to date and complies with current standards. In addition, clear guidelines and templates for creating and maintaining documentation can help to ensure consistent and high-quality results.
Q: What qualifications are required for commissioning plants?
A: Professionals involved in plant commissioning should have extensive knowledge of engineering or process engineering. Many have specialized in this field for many years and work freelance as independent consultants or auditors. They play a crucial role in ensuring that plants are commissioned efficiently, safely, and in accordance with applicable regulations. Their tasks often include planning and monitoring tests, analyzing systems and processes, and identifying and resolving potential problems before final commissioning.
In addition, they often have to communicate with various stakeholders, including engineers, project managers, and customers, to ensure that all aspects of commissioning are clearly understood and implemented on schedule. Problem-solving skills and a deep understanding of technical specifications are essential.
In addition, professionals in this field may be responsible for training the personnel who will later operate the plant, as well as for preparing comprehensive documentation and reports that describe the entire commissioning process in detail.
With the increasing complexity of modern plants, it is also important for these professionals to continuously educate themselves and stay informed about the latest developments and technologies in the field of process engineering. This enables them to develop innovative solutions and further optimize the efficiency and safety of the plants.
Q: How can you ensure that a plant complies with legal requirements?
A: To ensure compliance with legal requirements, all steps of the commissioning process should be carefully documented and reviewed by qualified auditors. Regular training and updates on current regulations are also important. In addition, a comprehensive quality management system should be implemented to ensure continuous improvement and adaptation to changing legal requirements. This can be achieved through regular internal audits and evaluations of operational processes.
Furthermore, it is advisable to set up an effective reporting system for deviations and potential violations in order to be able to react quickly to any problems that may arise. Employee training should not only take place when new regulations are introduced, but should be seen as an ongoing process to ensure that everyone involved is always up to date with the latest developments.
The use of technology, such as compliance software, can further facilitate monitoring and compliance and increase the efficiency of review processes. Finally, management should promote a culture of compliance in which compliance with regulations is seen as an integral part of the company's values.
This will ensure that the company is not only legally protected, but also builds trust with customers, partners, and regulatory authorities.
